Machining vs. Fabrication
“Metal machining” and “metal fabrication” are two terms that are often used interchangeably by people outside of the manufacturing industry. While these two phrases both refer to processes that involve transforming metal into specific parts or components, they are not necessarily the same and typically refer to different methods of manipulating the metal.
Whether you are in charge of project planning, administering parts procurement, or owning your own business, it is critical that you know the basics of each process. By familiarizing yourself with custom metal fabrication and metal machining, you will be better prepared to choose the correct service when ordering parts or planning out designs.
With that in mind, the team at Sierra Pacific Engineering and Products (SPEP) has created this guide to metal fabrication vs. machining to help you navigate the pros and cons of each. Below, we explore both metal shaping processes independently and then break down the differences between them.
What Is Metal Machining?
Metal machining is a general term used to refer to a specific set of manufacturing processes designed to create metal components from a solid block of raw material. During metal machining, the medium is shaped by grinding away fragments or cutting off large swatches of material similar to how an artist creates a sculpture. The end goal is to transform that piece of metal into your desired final shape and have uniform cuts.
The phrase “cutting” does not necessarily mean that the process involves a blade. Instead, metal machining can be performed using a variety of different cutting tools. The three main methods of machining are turning, milling, and drilling; each of which helps create certain features in the final product.
- Turning is the process of rotating the workpiece itself against the cutting tool with a device called a lathe. Lathing can be used to easily create intricate patterns which are uniform around the circumference of a part.
- Milling is another process used for machining custom parts and uses rotary cutters to shave off excess material from the workpiece. Milling is the most common machining process and can be used on multiple axes to make very complex shapes and patterns.
- Drilling is the process of making holes. This is done with a rotating bit that has cutting edges right at the tip which is pressed directly into the surface of the material.
What Is Custom Metal Fabrication?
Custom metal fabrication is another generic term used to describe a certain set of several different material shaping techniques. Though the name is often shortened to simply “metal fab”, metal fabrication typically refers specifically to processes that work with sheet metal as the raw material. The processes of creating sheet metal structures through fabrication are similar to how paper can be manipulated to create origami.
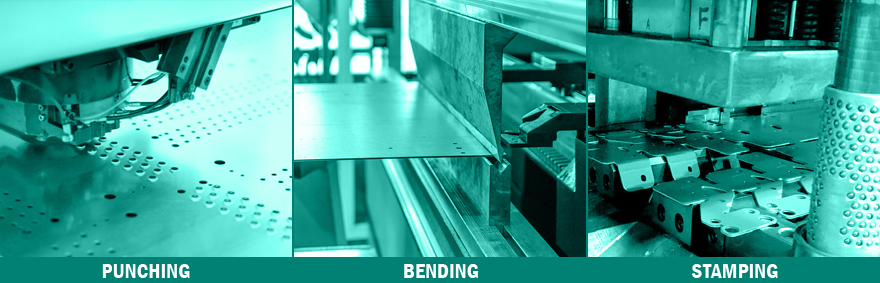
During metal fabrication, fabricators may use one or more of the following techniques:
- Punching uses a machine called a punch press to make a hole in the metal sheet by pushing (not cutting) through the material with a tool the same shape as the desired hole
- Bending produces a v-shape, u-shape, or corner in the material by folding it along a straight edge
- Stamping is the process of placing a flat sheet metal blank or coil into a stamping press where a tool forms the metal into a desired shape
Similarities of Machining and Fabrication
There are some steps, such as assembly, which can come into play for any type of metal manufacturing. When providing custom metalwork services, fabricators or machinists may combine several different produced components into a single final product. They might combine them using welds or assemble them using fasteners. Welding is a process in which two or more pieces are fused together by heat and permanently joined together as the pieces cool. Fastening is the process of securing two components together using an additional component such as a nut, bolt, screw, or rivet.
The final products of both machining and fabrication will also have similar properties since they are made from the same raw materials. Some advantages of making parts with metal are heat resistance, strength, and versatility. Most metals have a higher melting point than other materials and are less likely to deteriorate when exposed to extreme heat. Metal also tends to be stronger and more durable than if you were using plastic or other non-metallic components. Metals can also be handled using a wide variety of different processes, so you are not as restricted as you would be with other materials.
Differences in Machining and Fabrication
The most obvious difference between machining and sheet metal fab is the form of the metal that each process starts with. Machining begins with a solid block of material while fabrication begins with a sheet or roll. Because of this, each process is well suited to producing different types of final products. For example, machining is great for making anything solid with lots of fine details such as a valve or threaded bolt while fabrication is better suited for simple hollow structures like a box or enclosure.
Machining allows for a much higher degree of precision and accuracy than fabrication does. Although both processes can produce quality results, cutting creates a cleaner edge than shearing because the material is not stretched as much during the action. This results in machined parts being able to achieve much tighter tolerances than most sheet metal products. However, this precision comes at the expense of speed and efficiency. Both processes can be automated via specialized machinery, but progressive stamping is much faster than computerized machining and is therefore significantly less expensive, especially at high volumes. Unfortunately, there is no universal best choice, and each process works well for different situations.
Which Service Do I Need?
Any custom metalwork provider can provide a comprehensive list of their suite of services and specialties to help you understand if their services are right for you. Some companies can assist with the design of custom components in addition to manufacturing. Others can also use advanced metal fabrication techniques to create prototypes and then mass-produce the components needed for your project. Full-service suppliers may also help with project management and control the supply chain to ensure you have parts when you need them.
When you need high-quality components that are precision engineered to your specifications, it is always better to partner with a supplier like Sierra Pacific Engineering and Products (SPEP) which offers all of these services and more. SPEP has decades of industry experience and an extensive parts catalog of thousands of different industrial hardware products.
If you cannot find the components you need in our existing selection, our dedicated team of engineers can help you design the perfect custom component for your OEM application. We can assist with everything from development to prototyping to mass production of your parts.
Our team can manufacture custom metal access hardware devices using any common manufacturing process and in a wide range of different materials. We also offer a variety of different finishing and coating options to meet your specifications.
To learn more about SPEPs comprehensive lineup of custom metal fabrication services, contact us today. We will gladly connect you with one of our talented engineers or salespeople and get to work creating your precision parts.
Editor’s Picks

Sierra Pacific Engineering College Scholarship Program
Feb 7, 2022

What is Supply Chain Management, and Why Is It Important?
Jan 13, 2022

How To Make Threads in Solidworks: Become a Solidworks Expert
Nov 10, 2020